Sarufi Middleware
This feature allows two way communication between your chatbot and your server/API unlike the webhook feature which only allows one way communication from your chatbot to your server. This feature will allow you to send messages from your server to your chatbot and vice versa.
Lets see a sample use case of this feature.
Imagine you have a chatbot that allows users to order food. You want to send order number once the order is placed. You can use this feature to send the order number to the user in the chat or even a user track their order status.
Middleware feature uses a character @ to identify a variable that should be replaced with value obtained from server
How it works?
This feature works by allowing you to specify a URL that will be called by Sarufi when a chatbot needs to fetch responses. A POST request will be sent to your URL with a JSON body containing data from all previous states.
Below is an illustration to show what happens
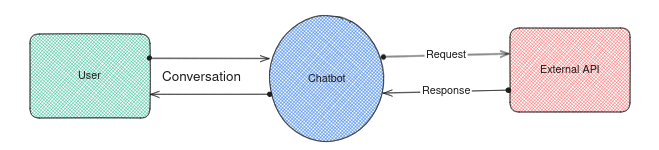
The diagram show the overview of what happens when you use middleware. The responses received from your server will be used to replace the variables in your chatbot responses. You can also use combination of both text and media.
The server responses should be of the format shown below:-
- Text
- Media
You can return as simple as a text or numerical values. You just need to follow the format below
{
"text": "value"
}
We support the following media types in our middleware feature, images, videos, audios, documents and stickers. The link provided should be pointing to a valid document type.
You can have any number of media in your response. The response should be of the formats shown below for each media type:-
- Image
- Video
- Audio
- Document
- Sticker
{
"medias": {
"images": [
{
"link": "https://example.com/office-location.jpg",
"caption": "Office Location"
}
]
}
}
{
"medias": {
"videos": [
{
"link": "https://example.com/deployment-video-3.mp4",
"caption": "How to deploy (Optional)"
}
]
}
}
{
"medias": {
"audios": [
{
"link": "https://example.com/how-to-get-started-01.wav",
"caption": "Beginner guide: Installation(optional)"
}
]
}
}
{
"medias": {
"documents": [
{
"link": "https://example.com/doc-agreement.pdf",
"caption": "Agreement"
}
]
}
}
{
"medias": {
"stickers": [
{
"link": "https://example.com/some-jokes-3.tif",
"caption": "Optional"
}
]
}
}
How to set middleware?
Navigate to your chatbot settings and click on the middleware tab. You will see a form like the one below
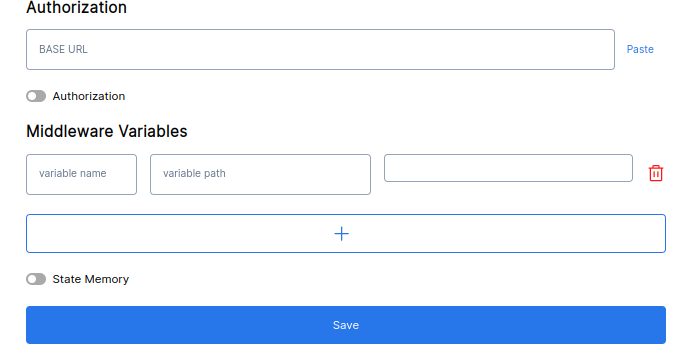
The image depicts the middleware settings page with two sections namely:- Authorization and Middleware variable
Authorization
You will have to provide a
base urland any authorization if available. Example:https://example.com/apisMiddleware variables
You will have to fill in variable name and variable path. A variable name is a name that a chatbot will refer to when it needs to obtain response from the path you provide. When adding a variable name do not use
@sign.A variable path is API route/endpoint that will receive a POST request with JSON body and return a well formated response. Make sure path provided accepts a
POSTrequest.Example:
A variable named,
order_numberthat has to obtain order number given user order details from path/order-numberof our base url. So the variable path will be /order-number. This will point tohttps://example.com/apis/order-number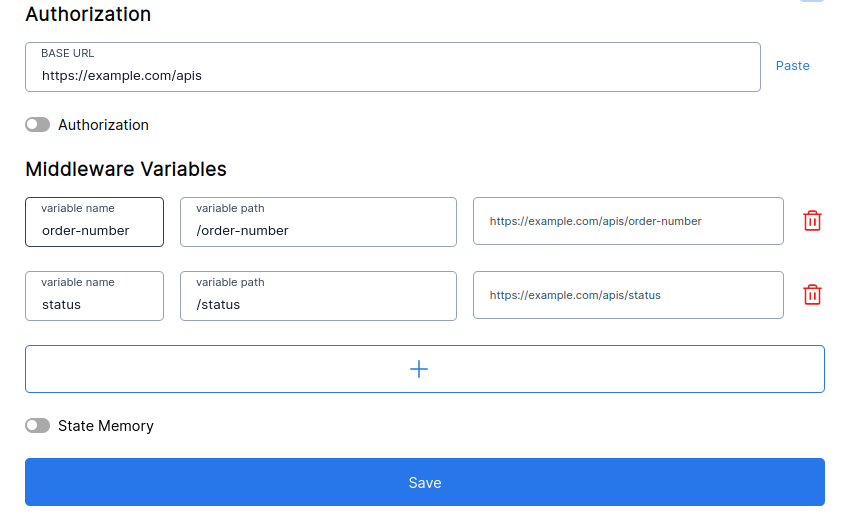
Once the bot reaches a flow with particular variable(order_number), a call will be made to a specified path with details from previous flow-states.
How to add variable in the flow?
As said before, the middleware feature uses a character @ to identify a variable that should be replaced with value obtained from external server. The character will be used with a variable that you define.
You just need a point in your flow tree to use a variable. Lets keep using our pizza chatbot example as always. Here we are going to let the chatbot bot provide a user with their order number after he/she confirms.
Below is diagram showing a more less the same flow we have been using along the guides. The diagram is expanded on choice_confirmation state in which order_confirmed state has variable named order_number
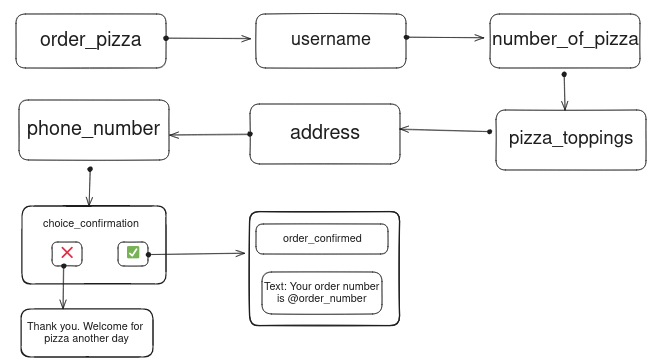
Below is the flow used.
{
"order_pizza": {
"message": [
[
"Hello, what's your name?"
],
[
"Can you provide your name please?"
]
],
"type": "text",
"next_state": "username",
"validators": [],
"images": [
{
"link": "https://sarufi-media.s3.amazonaws.com/d265fce7-3f73-4a40-b03f-f68ddbee6ebc.jpg",
"caption": "welcome to Pizza bot"
}
]
},
"username": {
"message": [
[
"Sure {{username}}, how many pizza would you like to order?"
],
[
"{{username}}, How many pizza would like?"
]
],
"type": "text",
"next_state": "number_of_pizzas",
"validators": [
{
"type": "custom_validation",
"regex": "^[1-9]?$",
"error_message": "🤦🏽♀️ Please provide valid number. Number between 1-9"
}
]
},
"number_of_pizzas": {
"message": [
[
"what would you like to have on your pizza"
],
[
"What would you like to have on your pizza?"
]
],
"type": "text",
"next_state": "pizza_toppings",
"validators": [
{
"type": "custom_validation",
"regex": "^[a-zA-Z]+$",
"error_message": "🤦🏾♀️ Please provide text only"
}
]
},
"pizza_toppings": {
"message": [
[
"Hey {{username}}, What is your address?"
],
[
"{{username}}, Cool, Whats your address ?"
]
],
"type": "text",
"next_state": "address"
},
"address": {
"message": [
[
"Sure, What is your phone number ?"
],
[
"Provide your phone number to proceed"
]
],
"type": "text",
"next_state": "phone_number",
"validators": [
{
"type": "phone_number_validation",
"error_message": "Please enter a valid phone number like 0711111111 or +255711111111 or +(222)222-2222"
}
]
},
"phone_number": {
"message": [
"Hey {{username}} you're placing {{number_of_pizzas}} pizza(s) with {{pizza_toppings}} to be delivered at {{address}}. ",
"",
"Please confirm",
""
],
"next_state": "choice_confirmation",
"type": "interactive",
"buttons": [
{
"1": "✅ I confirm"
},
{
"2": "❌ cancel"
}
]
},
"choice_confirmation": {
"1": "confirms",
"2": "does_not_confirm",
"fallback_message": [
"Please select 1 to confirm or 2 to cancel"
]
},
"does_not_confirm": {
"message": [
"You are welcome at our pizza service.",
"",
"We are always happy to serve you"
],
"type": "text",
"next_state": "end"
},
"confirms": {
"message": [
"Thank you for ordering with us. Your order number is @order_number"
],
"type": "text",
"next_state": "end"
}
}
The flow above has implemented variable placement and middleware. You can see variable order_number at the end of the flow.
Middleware in action
Lets see the bot in action
You can see the chatbot did obtain the order number. The API route order-number received a JSON body with all the data from previous states. The sample JSON is here
{
"order_pizza": "i want pizza",
"username": "jovine",
"number_of_pizzas": "1",
"pizza_toppings": "cheese",
"address": "kunduchi",
"phone_number": "+255748914671",
"choice_confirmation": "1"
}
You can processing the data sent to the endpoint/path provided and return a reponse that will be attached to chatbo's reponse message. This feature opens more possibilities to your chatbot.